Precision Machining in the Automotive Industry
Automotive parts machining is a vital process in providing precision components that are essential for car assembly. The automotive industry is particularly demanding when it comes to producing high quality and reliable parts with tight tolerances and strict process control. Specialized machine shops must be equipped with the right tools and expertise to efficiently handle the large volumes of automotive components required on a daily basis
The Main Car Engine Parts
Cylinder Block
The cylinder block is an important and integral part of the engine system. It serves as the foundation for the entire engine and accommodates a number of components, including the cylinder head and crankcase. Together, these three parts form the basis of structure and operation for any car engine.
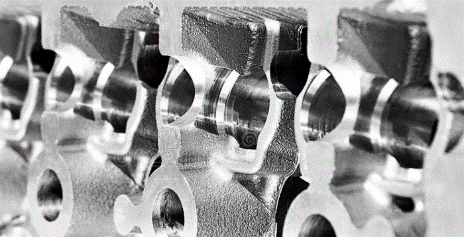
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is a key component of an engine, and is located between the cylinder block and its head. It forms an air-tight seal around each chamber and valve in order to contain combustion pressure. Additionally, it helps draw in fuel and oxygen for combustion, as well as divert exhaust molecules away from the engine’s cylinders after combustion is complete.

Crane Case
The crankcase is an important part of an engine, as it houses the crankshaft and other critical engine components. It is composed of two separate parts: the oil pan, which collects and stores excess oil from the engine, and the lower half of the cylinder block, which supports the crankshaft underneath it. Put together, these components form a complete crankcase assembly – sometimes referred to simply as a ‘crane case’.
Oil Pan
The oil pan of a vehicle is located in the bottom half of the crankcase, and it serves as a reservoir for engine lubricating oil. The oil pan is attached to the crankcase through set screws and with a gasket to make sure that no oil leaks out. This keeps the oil cool and helps keep it ventilated while also providing a place for its storage.

Gaskets
A gasket is a mechanical seal used to fill the space between two or more surfaces, objects, and materials. It is usually made from rubber, cork, paperboard, metal or other materials and is used to prevent leakage by providing a tight fitting joint between these surfaces.
Manifolds
A mobile manifold is an important part of a vehicle’s exhaust system. It consists of tubular pipes connected to the engine’s cylinder head which help direct the air-fuel mixture as well as exhaust gases. To handle the high temperatures of these gases, mobile manifolds are typically constructed out of durable cast iron materials.
Cylinder Liners
Cylinder liners are cylindrical shapes used inside the cylinders of an engine to prevent wear. These components are made from special alloy iron containing mixtures of silicon, manganese, nickel and chromium. They have excellent resistance to corrosion and wear and can be replaced when they become worn out. The manufacturing process involves casting centrifugally; this results in long lasting liners that offer improved performance for the engine.
Pistons
A piston is an essential part of the engine. It is a cylindrical plug that moves up and down within the cylinder to convert energy obtained from fuel combustion into mechanical power, which is then transferred to the crankshaft via the connecting rod. This crucial component helps engines generate and realize motion, making it one of the most significant components in an engine.
Piston Rings
Piston rings are used in engines to maintain the seal between the piston and the cylinder wall. In modern designs, 3 piston rings are typically utilized: 2 compression rings and 1 oil control ring. The purpose of these rings is to prevent air leaks so that the engine can properly combust fuel and transfer power. Furthermore, an oil control ring helps maintain optimal amounts of lubrication for smooth operation.
Piston Pins
Piston pins, also referred to as wrist or gudgeon pins, form the connection between the piston and the small end of a connecting rod. They are an integral component in engine design and allow the piston to move up and down in sync with the other parts that make up an internal combustion engine.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is the main source of power in an engine. It’s a rotating shaft which connects to the pistons and converts their up-and-down, reciprocating motion into a rotary motion that can be used to power the other engine parts. The crankshaft is at the heart of the power transmission system, transferring energy from the pistons to create horsepower.

Camshaft
The camshaft is an essential component of any internal combustion engine. It has cams mounted onto its shaft, which are used to convert the rotary motion of the camshaft into linear motion for follower components like valves. This allows for proper opening and closing of these valves, which results in a smooth running engine.

